What is Data?
Data is nothing but facts and statistics stored or free flowing over a network, generally it’s raw and unprocessed. For example: When you visit any website, they might store you IP address, that is data, in return they might add a cookie in your browser, marking you that you visited the website, that is data, your name, it’s data, your age, it’s data.
Data becomes information when it is processed, turning it into something meaningful. Like, based on the cookie data saved on user’s browser, if a website can analyse that generally men of age 20-25 visit us more, that is information, derived from the data collected.
What is a Database?
A Database is a collection of related data organised in a way that data can be easily accessed, managed and updated. Database can be software based or hardware based, with one sole purpose, storing data.
During early computer days, data was collected and stored on tapes, which were mostly write-only, which means once data is stored on it, it can never be read again. They were slow and bulky, and soon computer scientists realised that they needed a better solution to this problem.
Larry Ellison, the co-founder of Oracle was amongst the first few, who realised the need for a software based Database Management System.
What is DBMS?

A DBMS is a software that allows creation, definition and manipulation of database, allowing users to store, process and analyse data easily. DBMS provides us with an interface or a tool, to perform various operations like creating database, storing data in it, updating data, creating tables in the database and a lot more.
DBMS also provides protection and security to the databases. It also maintains data consistency in case of multiple users.
Here are some examples of popular DBMS used these days:
- MySql
- Oracle
- SQL Server
- IBM DB2
- PostgreSQL
- Amazon SimpleDB (cloud based) etc.
Characteristics of Database Management System
A database management system has following characteristics:
- Data stored into Tables: Data is never directly stored into the database. Data is stored into tables, created inside the database. DBMS also allows to have relationships between tables which makes the data more meaningful and connected. You can easily understand what type of data is stored where by looking at all the tables created in a database.
- Reduced Redundancy: In the modern world hard drives are very cheap, but earlier when hard drives were too expensive, unnecessary repetition of data in database was a big problem. But DBMS follows Normalisation which divides the data in such a way that repetition is minimum.
- Data Consistency: On Live data, i.e. data that is being continuosly updated and added, maintaining the consistency of data can become a challenge. But DBMS handles it all by itself.
- Support Multiple user and Concurrent Access: DBMS allows multiple users to work on it(update, insert, delete data) at the same time and still manages to maintain the data consistency.
- Query Language: DBMS provides users with a simple Query language, using which data can be easily fetched, inserted, deleted and updated in a database.
- Security: The DBMS also takes care of the security of data, protecting the data from un-authorised access. In a typical DBMS, we can create user accounts with different access permissions, using which we can easily secure our data by restricting user access.
- DBMS supports transactions, which allows us to better handle and manage data integrity in real world applications where multi-threading is extensively used.
Advantages of DBMS
- Segregation of applicaion program.
- Minimal data duplicacy or data redundancy.
- Easy retrieval of data using the Query Language.
- Reduced development time and maintainance need.
- With Cloud Datacenters, we now have Database Management Systems capable of storing almost infinite data.
- Seamless integration into the application programming languages which makes it very easier to add a database to almost any application or website.
Disadvantages of DBMS
- It’s Complexity
- Except MySQL, which is open source, licensed DBMSs are generally costly.
- They are large in size.
Components of DBMS
The database management system can be divided into five major components, they are:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures
- Database Access Language
Let’s have a simple diagram to see how they all fit together to form a database management system.
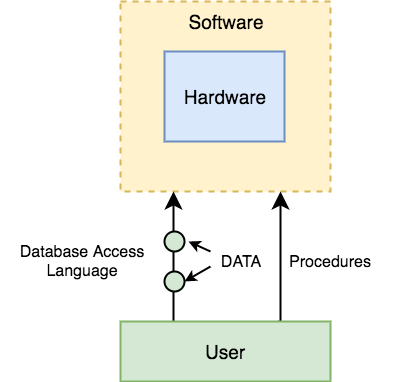
DBMS Components: Hardware
When we say Hardware, we mean computer, hard disks, I/O channels for data, and any other physical component involved before any data is successfully stored into the memory.
When we run Oracle or MySQL on our personal computer, then our computer’s Hard Disk, our Keyboard using which we type in all the commands, our computer’s RAM, ROM all become a part of the DBMS hardware.
DBMS Components: Software
This is the main component, as this is the program which controls everything. The DBMS software is more like a wrapper around the physical database, which provides us with an easy-to-use interface to store, access and update data.
The DBMS software is capable of understanding the Database Access Language and intrepret it into actual database commands to execute them on the DB.
DBMS Components: Data
Data is that resource, for which DBMS was designed. The motive behind the creation of DBMS was to store and utilise data.
In a typical Database, the user saved Data is present and meta data is stored.
Metadata is data about the data. This is information stored by the DBMS to better understand the data stored in it.
For example: When I store my Name in a database, the DBMS will store when the name was stored in the database, what is the size of the name, is it stored as related data to some other data, or is it independent, all this information is metadata.
DBMS Components: Procedures
Procedures refer to general instructions to use a database management system. This includes procedures to setup and install a DBMS, To login and logout of DBMS software, to manage databases, to take backups, generating reports etc.
DBMS Components: Database Access Language
Database Access Language is a simple language designed to write commands to access, insert, update and delete data stored in any database.
A user can write commands in the Database Access Language and submit it to the DBMS for execution, which is then translated and executed by the DBMS.
User can create new databases, tables, insert data, fetch stored data, update data and delete the data using the access language.
Users
- Database Administrators: Database Administrator or DBA is the one who manages the complete database management system. DBA takes care of the security of the DBMS, it’s availability, managing the license keys, managing user accounts and access etc.
- Application Programmer or Software Developer: This user group is involved in developing and desiging the parts of DBMS.
- End User: These days all the modern applications, web or mobile, store user data. How do you think they do it? Yes, applications are programmed in such a way that they collect user data and store the data on DBMS systems running on their server. End users are the one who store, retrieve, update and delete data.

